Tech Talk
5G and IoT: The Future of 5G Communications
Dear Readers,
This week’s blog is how 5G-enabled IoT is expected to enable technological advancement? Developing technologies like the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to grow with 5G.
Ambimat Electronics with its experience of over 4 decades as an ODM of IoT products wishes to draw the attention of its customers and readers of blog posts towards this upcoming field.
The fifth generation of cellular networking will usher in new opportunities for tech advancement and innovation.
The upcoming upgrade from 4G to 5G concerns pretty much anyone using a cellular connection. It’s wise to understand the 5G network. 5G’s ability to support a massive number of static and mobile IoT devices, which have a diverse range of speed, bandwidth, and quality of service requirements. Cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and edge computing will all help to handle the data volumes generated by the IoT, as 5G boosts network capacity. Further 5G enhancements, such as network slicing, non-public networks, and 5G core, will ultimately help to realize the vision of a global IoT network, supporting a massive number of connected devices.
What is 5G Technology?
5G is the next generation of mobile wireless communications, poised to replace the current 4G LTE connection in the upcoming years. 5G wireless connection assumes faster download/upload speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity.
For instance, 5G internet speed will be approximately 20 times faster than 4G, with the minimum download speed capped at 20 GB/s (while 4G can muster only 4 GB/s). Data transfer speed will be accelerated from approx—10 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps and beyond – a massive shift towards more seamless and effective connectivity.
Overall this will translate into the following benefits for businesses and consumers:
- Shorter delays: 5G will accommodate more massive data transfers and minimize the time when data is sent/received. This will enable real-time connectivity for IoT data exchanges, connected cars, and other “smart” objects plugged to the network.
- Increased connectivity: 5G mobile network architecture will significantly increase the capacity for resource provisioning. More people and devices will be able to communicate at the same time without overloading the network.
- Faster speed: As mentioned already, 5G speed will trump 4G, and likely become comparable (or even faster) to fiber-optic wired networks.
- Mobility: 5G enables base stations to support movement from 0 to 310 mph, meaning sustainable operations on-the-go (e.g., on a high-speed train).
- Improved connection density: 5G is expected to accommodate connected devices more than LTE and support up to 1 million connected objects per square kilometer. That’s significant considering the growth of IoT devices.
5G and the Internet of Things
5G is essential to the Internet of Things because of the need for a faster network with higher capacity that can serve connectivity needs. The 5G spectrum expands the frequencies on which digital cellular technologies will transfer data. This broader spectrum available for use increases the overall bandwidth of cellular networks, allowing for additional devices to connect.
Another area where 5G Ultra Wideband could impact the Internet of Things is enhancing virtual and augmented reality (AR/VR). 5G Ultra Wideband’s ultra-low latency can improve the AR/VR experience and opens possibilities for such Technology in business, education, and elsewhere.
5G and Business IoT
5G-enabled IoT is expected not only to enable technological growth; it is also projected to help support 22 million jobs around the world. This job growth is expected to come from the digitization of transportation, agriculture, manufacturing, and other physical industries. Consider also construction sites, mines, oil derricks, and freighter fleets: these industries would benefit significantly from ultra-fast data transmission to the time-sensitive nature of their output.
5G has the potential to drive advancements in smart machinery as well as smart manufacturing. Thinking even more significant, 5G could enable IoT to run virtually instantaneous traffic analyses, improve security and public safety and possibly enable remote surgery.
IoT presents both operators and industries with a fertile ground for innovations and new ways of engaging their end customers. Critical success factors will be to launch new services with a short time-to-market from idea to commercial offering combined with the right business models and access to a rich array of complementary offerings from ecosystem partners.
Terminal Action Analysis
Dear Readers, In the realm of EMV payment processing, understanding the intricate decision-making process that occurs within payment terminals is vital. The terminal’s role in determining whether to proceed with a transaction, seek online authorization, or reject it...
The facts and fiction of passwordless journey
Dear Readers, This week’s blog is about the passwordless authentication journey. Passwords require ongoing management from both users and IT staff. For the average user, keeping track of ever-multiplying passwords of varying complexity is, at minimum, a hassle and...
The Importance of Digital ID in Cybersecurity
Dear Readers, Digital identities have become a critical component of cyber security in today’s digital age. Digital identity is the gateway to accessing a large number of internet services, such as financial transfers, societal media, healthcare and more, as people’s...
The new information security default is zero trust.
Dear Readers, Today’s cybersecurity environment does not support a perimeter-based security approach. The traditional approach of protecting your organization’s network from outside threats using firewalls and access restrictions is no longer enough due to the threat...
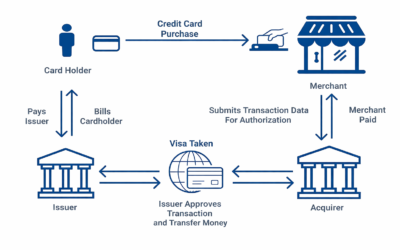
The primary players in payments processing
Dear Readers, In this blog we are going to learn about, Navigating the intricate world of payment processing involves understanding a web of players, each with unique roles and revenue-generating mechanisms. At the center are card networks like Visa, MasterCard,...
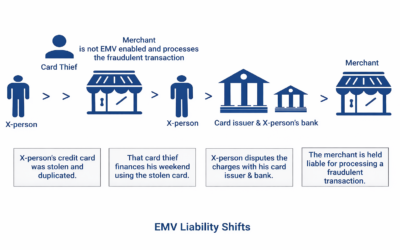
EMV Liability Shifts & Fallback Transactions
Dear Readers, How to navigate the EMV liability shift What you need to know about the EMV liability shift October 2015 marked the beginning of a new era for accepting payment cards in the US. That’s when the EMV liability shift took place, reassigning responsibility...


Recent Comments